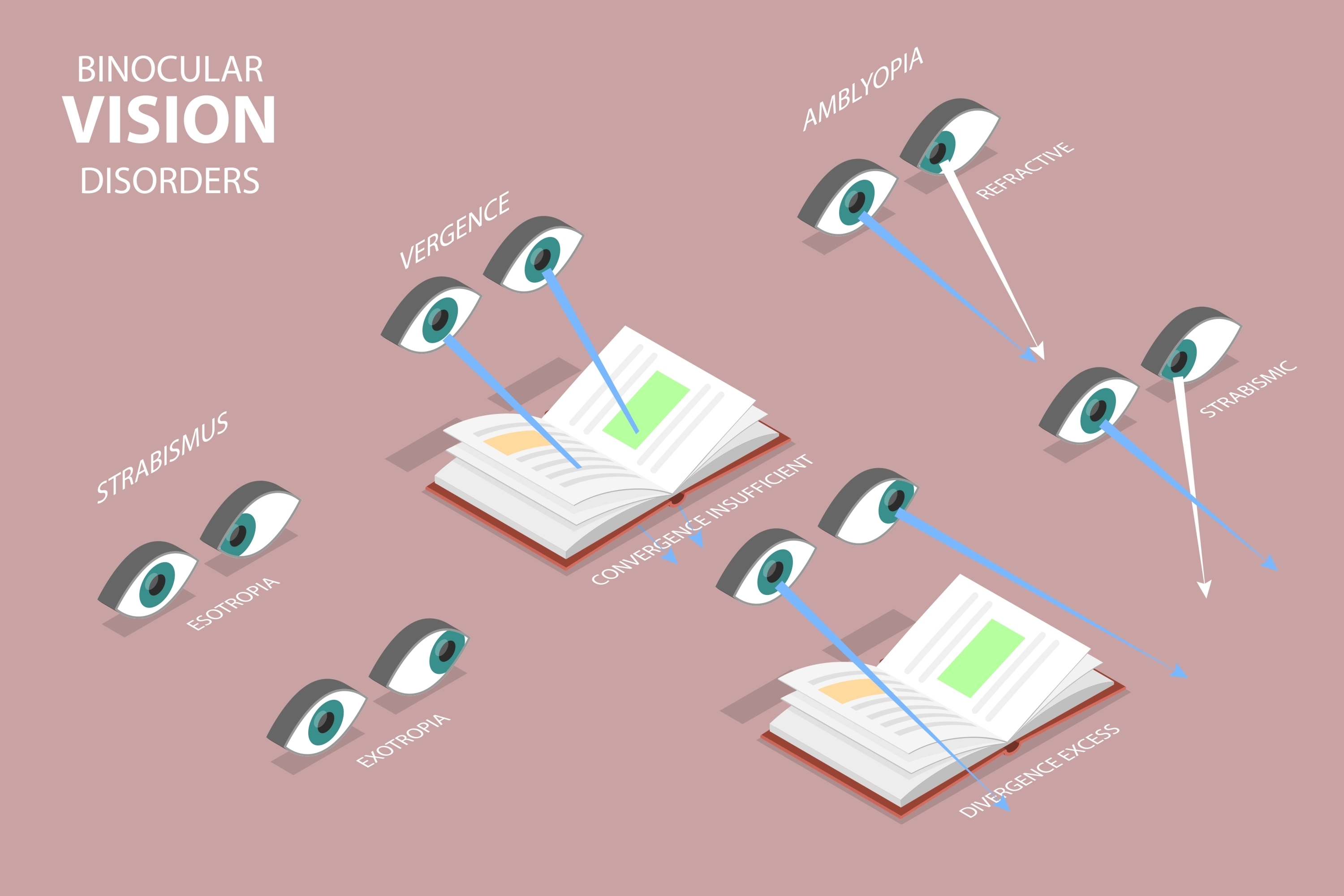
Convergence insufficiency (CI) is a condition that affects the way our eyes work together to focus on nearby objects. It can make everyday tasks like reading, writing, and using a computer difficult, often leading to frustration and a reduced quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for CI is key to managing this condition effectively.
What Causes Convergence Insufficiency?
At its core, convergence insufficiency occurs when the eyes struggle to align properly during close-up tasks. Normally, when we focus on something close, our eyes move inward (converge) to create a single, clear image. In people with CI, the ability to converge is weak, causing visual discomfort, double vision, and other symptoms.
The exact etiology of CI is not always clear, but several factors can contribute:
Developmental Issues: For some individuals, the condition may arise during childhood without any apparent underlying cause.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) or Acquired Brain Injury (ABI): These conditions can disrupt the neurological pathways responsible for coordinating eye movements, leading to CI.
Neurological Conditions: Other disorders that impact the nervous system may also play a role.
Common Symptoms of Convergence Insufficiency
Symptoms of CI often manifest during activities that require sustained near focus. These include:
Eye strain or discomfort
Headaches, particularly after reading or other close-up tasks
Double vision or blurred vision when focusing on near objects like a book or computer screen
Difficulty concentrating or staying focused
Avoidance of near tasks, such as reading or homework
In children and adolescents, these symptoms can often go unnoticed or be mistaken for other issues, such as a lack of interest in school.
Impact
Convergence insufficiency can have far-reaching consequences, particularly for students and professionals whose work requires significant near focus.
Academic Performance: Children with CI struggle to read, comprehend, and retain information, leading to poor grades and frustration. They may avoid schoolwork altogether, further hindering their academic progress.
Self-Esteem: The difficulties associated with CI can erode confidence. Children may feel "different" or "stupid" due to their struggles, impacting their self-worth and social relationships.
Career Choices: For adults, CI can limit career options, especially in professions that demand hours of detailed near focus.
Treatment for Convergence Insufficiency
The good news is that convergence insufficiency is treatable, and intervention at any age can lead to significant improvements.
Reading Glasses
In some cases, reading glasses or prism glasses may be prescribed to ease the strain of near tasks. However, it’s important to note that improperly prescribed glasses can exacerbate symptoms. Therefore, reading glasses should only be used under the guidance of an eye doctor.
Vision Therapy
Vision therapy is the preferred and most effective treatment for CI. This structured program of eye exercises is designed to strengthen the eye-brain connection and improve coordination. The Convergence Insufficiency Treatment Trial (CITT), a large-scale study, has demonstrated the efficacy of vision therapy in significantly reducing symptoms and improving quality of life for patients with CI.
Vision therapy typically involves:
Exercises to improve convergence ability and control
Activities to enhance binocular vision (the eyes’ ability to work together)
Gradual progression to tasks of increasing difficulty to build endurance and focus
Conclusion
Convergence insufficiency is a challenging but manageable condition. With proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals with CI can achieve significant relief from symptoms and improvements in their academic, professional, and personal lives. If you or someone you know is struggling with symptoms of CI, call us to schedule a comprehensive eye exam. Proper intervention can make all the difference in restoring comfort and confidence.